Creational Patterns ( 생성 패턴 )
These design patterns provides way to create objects while hiding the creation logic, rather than instantiating objects directly using new operator. This gives program more flexibility in deciding which objects need to be created for a given use case.
생성패턴은 객체의 생성로직을 숨기고 new 명령어를 통하지 않고 객체를 생성하는 방법들을 제공한다. 이는 특정 상황에서 어떤 방법으로 객체를 생성해야할지를 결정하는데 있어서 유연성을 제공한다.
Structural Patterns ( 구조적 패턴 )
These design patterns concern class and object composition. Concept of inheritance is used to compose interfaces and define ways to compose objects to obtain new functionalities.
구조적 패턴들은 클래스와 객체의 구성에 관여한다.
Behavioral Patterns ( 행위적 패턴 )
These design patterns are specifically concerned with communication between objects.
이 패턴들은 객체들 사이의 커뮤니케이션에 관심을 가진다.
오늘 살펴볼 Proxy 패턴은 Structural 패턴에 속한다.
프 록시 패턴은 네트워킹을 공부해본 사람이라면 이해하기가 쉬울 것이다. 프록시가 뭔지를 알테니까 말이다. 여기서 말하는 프록시란 프록시 서버에서 말하는 그것과 동일한 개념이다. 일종의 중간연결자 역할을 하는 클래스를 만들어서, 요청이 들어오면 최초 요청일 경우 새로 생성하고 생성된 객체를 응답으로 보내고, 두번째 요청부터는 기존에 생성했던 것을 응답으로 보내는 것이다.
이해가 잘 안간다면 좀 더 자세히 알아보자.
Proxy Pattern Structure
우선 이 클래스 다이어그램부터 이해를 해보도록 하자. 여기서 중요한 것은 RealSubject와 Proxy 그리고 Subject사이의 관계이다. 클라이언트는 Subject객체의 Request()를 호출하고 Subject객체를 받는다. RealSubject와 Proxy는 Subject를 상속하는 클래스들인데 Proxy클래스의 Request()는 경우에 따라 RealSubject의 Request()를 호출한다. RealSubject의 Request()에서는 클라이언트가 원하는 Subject객체를 반환한다.
따라서 runtime에는 호출 순서가 아래와 같다고 할 수 있다. Proxy는 RealSubject를 가지고 있는데 이것이 null이 아닌 경우 그대로 반환하고 null인경우 RealSubject의 Request()를 요청하여 새로운 객체를 생성하고 그것을 Proxy 내부에 가지고 있게 된다.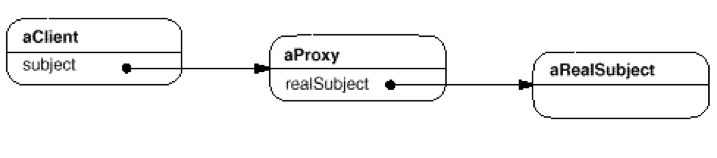
패턴의 목적 ( Intent ) :
프록시 패턴의 목적은 또다른 객체에 대한 접근을 컨트롤하기 위해서 그 객체를 담을 수 있는 그릇을 제공하는 것입니다.
패턴이 나오게 된 동기 ( Motivation ) :
워
드프로그램에서 사진파일을 넣게되면 로딩이 느려지는 현상이 발생할 때가 있었다. 지금이야 워낙 컴퓨터 사양이 좋아져서 그런일을 많이
보지는 못하지만 사진파일 사이즈역시 좋은 화질인 경우 상당한 사이즈를 자랑하기 때문에 무시할 수 없다. 이런 경우 페이지를
이동할 때마다 디스크에 있는 이미지 파일을 계속 요청하는 것이 아니라 한번만 요청하여 프록시에 가지고 있다가 다시 요청이 들어오면
프록시에서 이미지를 가져와서 디스플레이 해주는 방식이 필요하게 된 것이다. 이런식으로 속도의 향상을 꿰한것이다. 아래 그림은
디스크에 있는 이미지 파일에서 데이타를 읽어와서 메모리에 상주하는 프록시에 넣고 문서에서 이에 접근하는 것을 보여주고있다.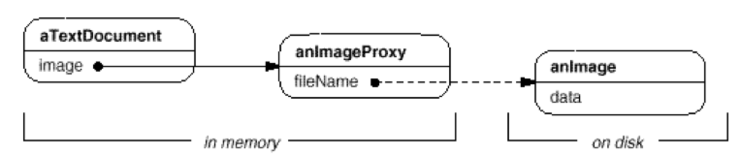
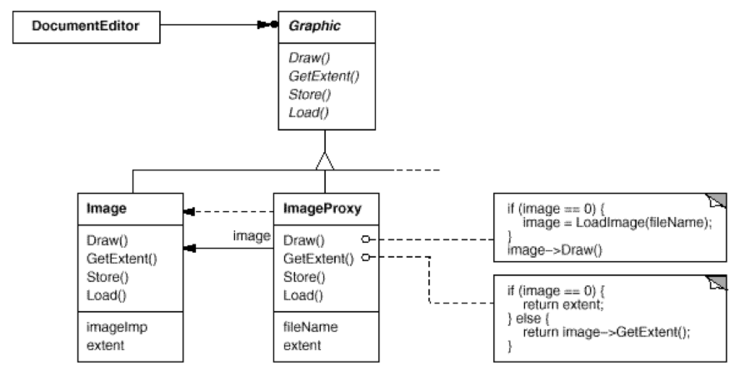
위에서 봤던 클래스 다이어그램에 문서프로그램의 예를 적용시켜 본 것이다. ImageProxy의 우측을 보면 image가 0인지를 판별하고 0일경우 Image를 가져와서 보여준다는 것을 알려주는 간략한 소스가 보인다.
유용성 ( Applicability ) :
Proxy is applicable whenever there is a need for a more versatile or sophisticated reference to an object than a simple pointer. Here are several common situations in which the Proxy pattern is applicable:
프록시 패턴은 아래와 같은 상황에서 유용합니다.
1. A remote proxy provides a local representative for an object in a different address space. NEXTSTEP [Add94] uses the class NXProxy for this purpose. Coplien [Cop92] calls this kind of proxy an "Ambassador."
2. A virtual proxy creates expensive objects on demand. The ImageProxy described in the Motivation is an example of such a proxy.
3. A protection proxy controls access to the original object. Protection proxies are useful when objects should have different access rights. For example, KernelProxies in the Choices operating system [CIRM93] provide protected access to operating system objects.
4. A smart reference is a replacement for a bare pointer that performs additional actions when an object is accessed. Typical uses include
o counting the number of references to the realobject so that it can be freed automatically when there are no more references (also called smart pointers [Ede92]).
o loading a persistent object into memory when it's first referenced.
o checking that the realobject is locked before it's accessed to ensure that no other object can change it.
등장 인물 ( Participants ) :
• Proxy (ImageProxy)
o maintainsareferencethatletstheproxyaccesstherealsubject.
Proxy may refer to a Subject if the RealSubject and Subject interfaces are the same.
o provides an interface identical to Subject's so that a proxy can by substituted for the real subject.
o controls access to the real subject and may be responsible for creating and deleting it.
o other responsibilities depend on the kind of proxy:
ß remote proxies are responsible for encoding a request and its arguments and for sending the encoded request to the real
subject in a different address space.
ß virtual proxies may cache additional information about the real subject so that they can postpone accessing it. For
example, the ImageProxy from the Motivation caches the real
image's extent.
ß protection proxies check that the caller has the access permissions required to perform a request.
• Subject (Graphic)
o defines the common interface for RealSubject and Proxy so that a Proxy can be used anywhere a RealSubject is expected.
• RealSubject (Image)
o defines the real object that the proxy represents.
원리 ( Collaborations ) :
• Proxy forwards requests to RealSubject when appropriate, depending on the kind of proxy.
패턴 사용의 장단점 ( Consequences ):
The Proxy pattern introduces a level of indirection when accessing an object. The additional indirection has many uses, depending on the kind of proxy:
-
A remote proxy can hide the fact that an object resides in a different address space.
-
A virtual proxy can perform optimizations such as creating an object on demand.
-
Both protection proxies and smart references allow additional house keeping tasks when an object is accessed.
There's another optimization that the Proxy pattern can hide from the client. It's called copy-on-write, and it's related to creation on demand. Copying a large and complicated object can be an expensive operation. If the copy is never modified, then there's no need to incur this cost. By using a proxy to postpone the copying process, we ensure that we pay the price of copying the object only if it's modified.
To make copy-on-write work, the subject must be reference counted. Copying the proxy will do nothing more than increment this reference count. Only when the client requests an operation that modifies the subject does the proxy actually copy it. In that case the proxy must also decrement the subject's reference count. When the reference count goes to zero, the subject gets deleted.
Copy-on-write can reduce the cost of copying heavyweight subjects significantly.
관련 패턴들 :
Adapter : An adapter provides a different interface to the object it adapts. In contrast, a proxy provides the same interface as its subject. However, a proxy used for access protection might refuse to perform an operation that the subject will perform, so its interface may be effectively a subset of the subject's.
Decorator : Although decorators can have similar implementations as proxies, decorators have a different purpose. A decorator adds one or more responsibilities to an object, whereas a proxy controls access to an object.
Proxies vary in the degree to which they are implemented like a decorator. A protection proxy might be implemented exactly like a decorator. On the other hand, a remote proxy will not contain a direct reference to its real subject but only an indirect reference, such as "host ID and local address on host." A virtual proxy will start off with an indirect reference such as a file name but will eventually obtain and use a direct reference.
추가 정보 :
- Adapter provides a different interface to its subject. Proxy provides the same interface. Decorator provides an enhanced interface.
- Decorator and Proxy have different purposes but similar structures. Both describe how to provide a level of indirection to another object, and the implementations keep a reference to the object to which they forward requests.
프록시 패턴을 사용한 간단한 예제입니다.
interface Image { public void displayImage(); } //on System A class RealImage implements Image { private String filename; public RealImage(String filename) { this.filename = filename; loadImageFromDisk(); } private void loadImageFromDisk() { System.out.println("Loading " + filename); } public void displayImage() { System.out.println("Displaying " + filename); } } //on System B class ProxyImage implements Image { private String filename; private Image image; public ProxyImage(String filename) { this.filename = filename; } public void displayImage() { if (image == null) { image = new RealImage(filename); } image.displayImage(); } } class ProxyExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Image image1 = new ProxyImage("HiRes_10MB_Photo1"); Image image2 = new ProxyImage("HiRes_10MB_Photo2"); image1.displayImage(); // loading necessary image2.displayImage(); // loading necessary
image1.displayImage(); // loading unnecessary image2.displayImage(); // loading unnecessary } }
또 다른 목적( 리눅스에서 권한에 따라 명령어 실행을 막거나 통과시키는)으로 사용된 프록시 패턴의 예제는 아래 링크에서 보실 수 있습니다.
http://www.journaldev.com/1572/proxy-design-pattern-in-java-example-tutorial
출처 : http://sourcemaking.com/design_patterns/proxy
Design Patterns : Element of Reusable Object Oriented Software ( by GoF, 1994 )
http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%94%84%EB%A1%9D%EC%8B%9C_%ED%8C%A8%ED%84%B4
'💻 Programming > GoF Design Pattern' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [디자인패턴] 퍼사드 패턴 ( Facade Pattern ) (0) | 2015.11.03 |
|---|---|
| [디자인패턴] 브리지 패턴 ( Bridge Pattern ) (0) | 2015.11.03 |
| [디자인패턴] 데코레이터 패턴 ( Decorator Pattern ) (0) | 2015.11.03 |
| [디자인패턴] 어댑터 패턴 ( Adapter Pattern ) (0) | 2015.11.03 |
| [디자인패턴] 책임전가 패턴 ( Chain of Responsibility Pattern ) (0) | 2015.11.03 |


